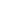
Thrombosis is a medical term referred to as the formation of blood clots in your blood vessel. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) means the blood clots are formed in one of your body’s deeper veins. Usually, Deep vein thrombosis is observed in the lower leg. Sometimes it also occurs in the thigh or pelvis area. The condition is rarely seen in the arm, brain, intestines, liver, or kidney.
DVT is considered a medical emergency. The CDC board say that 10–30% of people diagnosed with DVT condition in the leg met with fatal health complications within a month.
Though DVT is not a life-threatening condition, if the blood clot breaks free and travels through your bloodstream and gets stuck in the blood vessels of your lungs, it leads to a condition called pulmonary embolism. This might be turned to a life-threatening condition that needs immediate diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Symptoms include:
- Swelling of your leg or arm, usually on one side
- Pain or tenderness in your affected leg
- Severe pain in your foot and ankle
- The area on your affected leg or arm hurts and feels warmer than usual
- Skin that is red or discoloured
- The veins on the surface of the skin might become swollen
- Skin in the affected area might turn into a reddish or bluish colour
Symptoms of a Pulmonary Embolism include
- Shortness of breath sudden or breathing fastly
- Sharp chest pain when you take a deep breath or while coughing
- Back pain
- Cough associated with blood/phlegm
- Unusual sweating
- High heartbeat
- Feeling dizzy or fainting
Sometimes you may even know that you have deep vein thrombosis until it becomes severe or causes pulmonary embolism.
Causes Of Deep Vein Thrombosis
When the flow of blood in your veins is too slow, sometimes it might result in blood clots leading to deep vein thrombosis. It is also caused if you have certain disorders, injury to your veins, surgery, specific medications, and limited movement. These conditions can happen in the below cases:
- Inheriting a blood-clotting disorder
- Hormone replacement therapy
- Resting in bed for a long period, for example, in a hospital after surgery,
- Long stay in bed and not moving much can limit your blood circulation in
- your legs.
- Injury or surgery to your veins
- Using birth control pills
- Smoking thins your blood and increasing the risk of clotting
- Being overweight or obese
- Some forms of cancer and it’s treatment might also increase the risk of
- blood clots
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Heart diseases
- Pregnancy might develop pressure on your veins in the pelvis and legs
It is estimated that on an average, 1 out of every 1,000 people might develop symptomatic deep vein thrombosis(DVT) per year. The risk of DVT increases with age and somewhat more prevalent in men compared to women.
How Is Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosed?
If a person suspects having DVT, then immediate medical attention is necessary. The doctor will check for symptoms and a physical examination. However, symptoms alone can’t determine DVT, and the doctor might recommend some tests, which include:
- Ultrasound
- Blood test.
- Venography
- CT scans or MRI
Treatment For Deep Vein Thrombosis
The main goal of Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) treatment is to prevent the blood clot from increasing its size and from breaking loose, which causes a pulmonary embolism. The treatment also aims to reduce the chances of occurring deep vein thrombosis to happen again.
Medication: Blood thinners like anticoagulants are the common drugs used to treat Deep vein thrombosis.
When medication can’t help, doctors prefer to use clot busters or thrombolytics.
Compression stockings: special socks that prevent pressure and blood from pooling in your veins.
IVC filter placement: If you are not able to use blood thinner or if they are not effective for you, your doctor inserts a small cone-shaped object called a filter into your inferior vena cava, the largest vein in your body. I
t is called the Inferior vena cava (IVC) filter, and the filter can prevent the large clots from reaching your lungs. The IVC filter placement procedure is done by an interventional radiologist, a doctor who specializes in image-guided procedures.
Suction Thrombectomy: Suction or aspiration thrombectomy is a safe and effective procedure performed using a large-size catheter for acute deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in lower extremities.
The procedure is done by a radiologist in an angiography suite. A small incision is made in the artery and a device that consists of a catheter, a separator, and a vacuum pump is sent into the vein. Once the catheter reaches the thrombus it is moved into position placing the microcatheter at the proximal part of the thrombus.
Now negative pressure is applied with the help of a syringe. When the syringe is pulled back the clots are sucked out as fragments or captured by the negative pressure at the catheter tip and retracted as a single piece.
Mechanical Thrombectomy: It is another endovascular procedure done by a radiologist who performs thrombectomy. In this procedure, the radiologist inserts a catheter sheath called a catheter through the incision in the femoral artery near the groin or the vein below your knee.
Now, the radiologist inserts a guidewire into the femoral vein through the sheath, pushes the wire beyond the clot, then a catheter is passed over the wire into the blocked area. The device at the catheter tip or a mechanical tool breaks up the clot and removes them successfully.
Catheter guided thrombolysis: These minimally invasive procedures like thrombolysis are often done by a specially trained interventional radiologist. You will be placed on the surgical table and connected to monitors to observe your blood pressure, oxygen level and pulse.
The area where the catheter to be inserted is sterilized, and a small incision is made at that area. Now the radiologist will insert a catheter through the incision into a blood vessel and drive it to the thrombus.
A contrast dye is injected and a series of images are taken to find the exact location of the clot. The radiologist reviews the images and decides whether the clot to be treated by dissolving it through medication or by breaking it with mechanical devices, or sometimes both.
If the blood clot is treated by dissolving through medication, then the catheter is left in place by connecting it to a special device. The device delivers the medicine at a specific rate.
These clot-dissolving medications need to be delivered over several hours to a few days. In most of the cases, the clots are able to dissolve within 24 hours. All this you will be monitored by the doctor closely.
Post-thrombotic syndrome(PTS): Post-thrombotic syndrome is a complication developed in people with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) of the leg. It causes chronic pain, swelling, and some other symptoms associated with your leg. It develops within weeks or months after DVT.
Compression with the help of compression stockings is the main treatment for PTS. It increases the flow of blood in your veins. You may also be suggested using intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) device to apply pressure on your affected veins in your leg.
Some simple lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, losing weight, and being active, avoiding sitting for long periods, can keep your blood to circulate in a proper way and lowers your odds of DVT condition.
To know more detailed information, contact Dr. Pradyumna Reddy, one of the best Interventional Radiologist in Hyderabad. He has immense experience in handling Deep Vein Thrombosis conditions successfully.